What is Women Reservation Bill in India? This bill proposes to reserve one-third of all seats in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies for women.
It is important because it would increase women’s representation in government and promote gender equality.
According to the Constitution 108th Women Reservation Bill, 2008, women should be given one-third (33%) of the seats in state legislative assemblies and the Parliament. The law calls for sub-reservation for SCs, STs, and Anglo-Indians within the 33% quota. Many states or union territories have the option of allocating reserved seats in rotation. The approved law provides that the seats reserved for women shall be eliminated 15 years after the commencement date of the Amendment Act.

What is Women Reservation Bill in India?
According to sources, several BJP ministers and MPs have been urged to bring female voters to Parliament in the upcoming days.
JP Nadda, the president of the BJP, met with a number of them on Monday. A number of individuals have called for the passage of the Women Reservation Bill, which guarantees a 33% quota in the Lok Sabha and state legislatures.
The Congress Working Committee also passed a resolution on the issue at its meeting on Sunday in Hyderabad.
The Women’s Reservation Bill’s tumultuous legislative history started 27 years ago, in September 1996, when it was tabled in Parliament by the H. D. Deve Gowda-led administration.
Since then, almost every administration has attempted to approve it, the UPA administration even succeeded in doing so in the Rajya Sabha in 2010, however, owing to a lack of political will and consensus, the endeavor was unsuccessful.
Read about How PM Vishwakarma Scheme Benefits people 2023
Why women reservation bill is important?
The Women’s Reservation Bill is of great importance for the following reasons:
To boost women’s participation in politics
In terms of the proportion of women in parliament, India comes in at number 144 out of 191 nations. Despite the fact that 48% of Indians are female, this is the case.
A 33% seat reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies under the Women’s Reservation Bill would help to address this gender disparity. This would give women a bigger voice in decision-making and increase the number of women in politics.
Gender inequality and discrimination are widespread in India. Women are often denied equal opportunities in education, employment, and other areas of life.

To address gender inequality and discrimination in India
The Women’s Reservation Bill would help to address gender inequality and discrimination by increasing the representation of women in politics. Women politicians would be able to advocate for women’s rights and interests and work to create a more equitable society.
In addition to these two main reasons, the Women’s Reservation Bill is also important for a number of other reasons, such as:
- To promote the empowerment of women.
- To improve the quality of governance.
- To increase the diversity of perspectives in government.
- To serve as an inspiration for other countries.
Key points on the Women’s Reservation Bill
- In 1996, the bill was initially presented to the Lok Sabha.
- The Lok Sabha has approved the bill several times, but the Rajya Sabha has never done so.
- According to the proposed legislation, women would be given 33% of the seats in the Lok Sabha and state legislative bodies.
- The bill is supported primarily by the claims that it will increase the number of women in politics and that it will aid in the fight against discrimination and gender inequality in India.
- Heated debates & sexist taunts – The WRB has seen some contentious discussions and a fair amount of misogyny.
- Quota within quota – The 1996 committee advocated a quota for OBC women under the Bill’s one-third reservation for women, however, this recommendation was never implemented.
- Opponents claim that the WRB will not help their ladies as a result of this.
- Lack of political ability – Only the Biju Janata Dal (BJD) of Odisha and the Trinamool Congress (TMC) of West Bengal have seats set aside for female candidates in elections.
- Diverts attention – WRB’s detractors claim it draws attention away from more important electoral reform concerns including the criminalization of politics and party democracy.
Key Issues of the Women’s Reservation Bill
- Reservation laws are in dispute. Affirmative action is deemed necessary by supporters to assist women. Reservations may empower women and allocate resources, according to recent panchayat research.
- Because they wouldn’t compete on merit, opponents claim it would prolong gender inequality. They claim that this strategy serves as a diversion from issues with election reform, such as the criminalization of politics and intra-party democracy.
- The number of seats in Parliament reserved for women restricts voter choice. As a result, some analysts advise dual-member seats and political party reservations.
- The possibility of not being re-elected may make an MP less motivated to work for his constituency if reserved seats are rotated at every election.
- The 1996 Women’s Reservation Bill report promoted reservations for OBC women after the Constitution was changed to allow the OBC quota. Additionally, the Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils were recommended for reservation. The Bill does not contain either recommendation.
What should we do next?
- In India, there are a lot of women, which represents a lot of potential that, if unlocked, could advance the country.
- By giving the vast majority of people a voice in how their lives should be run, the inclusion of women will spark democracy.
Why is it difficult to pass the Bill?
One of the main obstacles to the Rajya Sabha’s adoption of the Women’s Reservation Bill is the current electoral system, which uses the single transferable vote method. This method gives votes to candidates who are more likely to win, making it challenging to reserve seats for particular groups.
There are currently no reservations for SCs and STs in the Rajya Sabha, and any effort to add them would require amending the constitution’s voting procedures.
Why is Women Reservation Bill important?
Historically, societal restrictions and discrimination have harmed women.
Caste groups – Any plan for women’s reservation must adhere to constitutional principles and take caste diversity into consideration.
Gender quota – Women’s representation would remain minimal without a gender quota, severely undermining our democracy.
Panchayats – Recent research on panchayats has shown the beneficial impact of reservation on the distribution of resources and the empowerment of women.
Vote share – Despite an increase in the percentage of women voting, there are still not enough women in positions of authority.

What is the situation of Women’s Reservations in India?
Gujarat- Only 8% of the candidates for its 182-member parliament were women.
In Himachal Pradesh, where women make up one of every two voters, 67 men and just one woman have been elected.
National average – 8% of women serve in state legislatures across the country.
Rankings – India is ranked 144th out of 193 countries in the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s survey regarding the representation of women in parliament.
Why was the bill not approved by the parliament?
- The WRB has witnessed some contentious discussions and a good deal of misogyny. Heated debates and sexist taunts.
- A quota within a quota was proposed by the 1996 committee as part of the Bill’s one-third reservation for women, but this recommendation was never carried out.
- Because of this, critics assert, the WRB will not aid their women.
- Lack of political aptitude – Only the Trinamool Congress (TMC) of West Bengal and the Biju Janata Dal (BJD) of Odisha have seats reserved for female candidates in elections.
- WRB’s critics assert that it diverts attention from issues related to electoral reform that are more pressing, such as the criminalization of politics and party democracy.
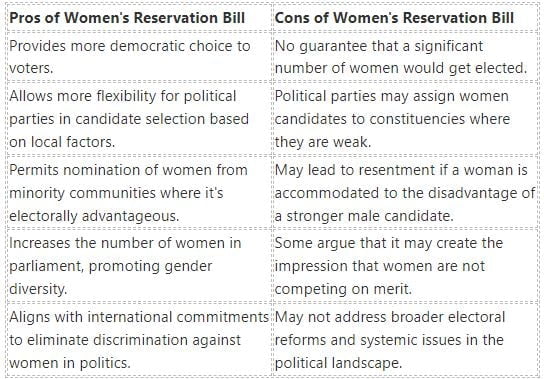
Women Reservation Bill Pros and Cons
Women Reservation bill pros and cons are:
Pros:
- The empowerment of women will result from affirmative action. For instance, the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, which provides women with a reservation at the panchayat level, has resulted in more responsiveness, gender-sensitive decisions, etc.
- Politics will be decriminalized since fewer women legislators will face criminal charges.
Cons:
- Draws attention away from significant electoral reforms like party democracy within the party, etc.
- Restricts voters’ options.
- Reservable constituency rotation may reduce an MP’s motivation to work.
Know more about PM-eBus Sewa Scheme : Revolutionizing India’s Green Public Transportation 2023
Conclusion:
The Women’s Reservation Bill has a number of arguments. One argument is that it would result in better policies for women and girls because it would increase the representation of women in the government. Another claim is that by giving women a voice in the decision-making process, it would advance gender equality. It would also act as a role model for young girls, demonstrating to them that they are capable of achieving anything they set their minds to.
FAQs
Q.1 The Women’s Reservation Bill: What is it?
Ans: A bill to give women a third of the seats in the Lok Sabha and state legislatures.
Q.2 Why is it crucial?
Ans: To ensure that women are fairly represented in Indian politics.
Q.3 What advantages are there?
Ans: Assert gender equality, increase the number of women in politics, and strongly convey India’s commitment to gender equality.
Q.4 What are the difficulties?
Ans: Requires amending the Constitution and is opposed by some political parties and organizations.
Q.5 What steps can be taken to overcome the difficulties?
Ans: Build public support for the proposal and collaborate with political parties to achieve agreement.
Q.6 What is the bill’s future?
Ans: Uncertain, but public support is rising.
