Most people are unaware of what is REIT. A real estate investment trust is a company that owns, operates, or finances income-generating real estate.
We are here to explain if any confusion you may have regarding REIT. and to highlight some of the best real estate investment strategies in this article.
What is REIT?
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) have become an increasingly popular way for both novice and experienced investors to earn passive income and diversify their portfolios through real estate. This comprehensive guide will explain everything you need to know about REITs to start investing.
Real estate investment trusts is a company that owns, operates, or finances income-generating real estate. Some examples include apartment buildings, warehouses, hotels, shopping malls, offices, cell towers, and more.
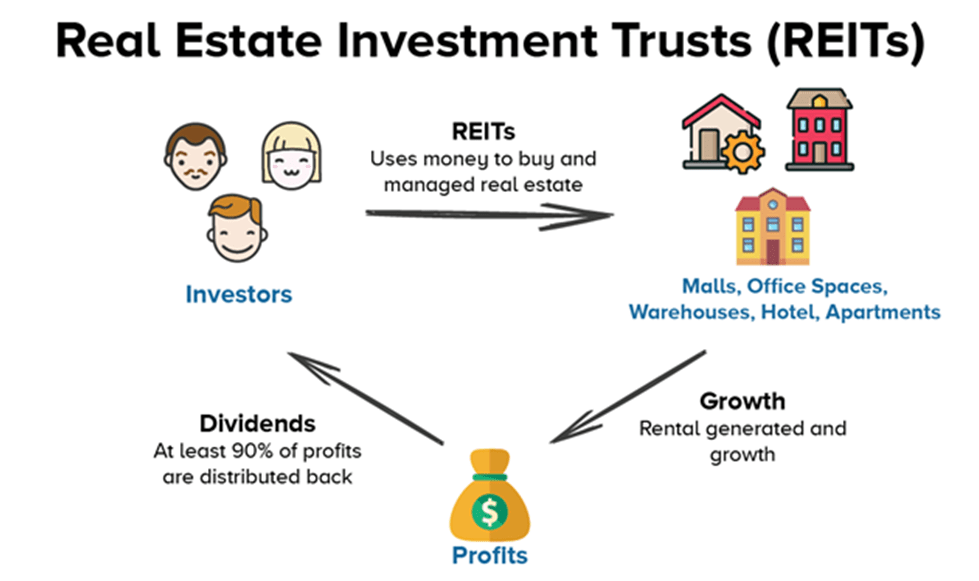
Real estate investment trusts are corporations or trusts that allow individual investors to invest in real estate without having to buy, manage, or finance properties themselves. By purchasing shares of a REIT, you can earn dividends from the income produced through their real estate investments.
There are a few key features that qualify a company as a Real estate investment trusts:
- It must invest at least 75% of total assets in real estate.
- It must earn at least 75% of gross income from rents or interest from real estate financing.
- It must have a diverse ownership with at least 100 shareholders and no more than 50% owned by five or fewer individuals.
- It must distribute at least 90% of taxable income to shareholders as dividends annually.
This structure allows even small investors to benefit from owning shares of large-scale, income-producing real estate.
| Top 10 Digital Marketing Source | Top 10 Niches to Make Money Online |
| Tax Saving Investment Schemes | Top 10 Passive Income Ideas |
Types of Real Estate Investment Trusts
There are two main types of Real estate investment trusts:
Equity REITs: Equity REITs own and operate income-producing real estate properties. The majority of REITs are equity REITs. They generate income through rents earned from tenants. Some common types of equity REITs include:
- Retail REITs – Own and manage retail rental properties like malls, outlets, shopping centers. Examples: Simon Property Group, Realty Income, National Retail Properties.
- Residential REITs – Own and operate rental apartment buildings and housing communities. Examples: AvalonBay Communities, Equity Residential, UDR Inc.
- Office REITs – Own and manage office rental spaces. Examples: Boston Properties, Alexandria Real Estate Equities, SL Green Realty.
- Healthcare REITs – Own medical facilities like hospitals, medical offices, senior housing. Examples: Welltower, Ventas Inc, Healthcare Trust of America.
- Industrial REITs – Own and operate industrial rental spaces like warehouses, distribution centers, storage facilities. Examples: Prologis, Duke Realty, STAG Industrial.
Mortgage REITs Mortgage REITs provide financing for real estate by issuing or investing in mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. They earn income from mortgage interest and fees. Some examples of mortgage REITs include Annaly Capital Management, AGNC Investment Corp, and Two Harbors Investment Corp. Mortgage REITs tend to be more leveraged than equity REITs and carry higher risk.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
There are several advantages to investing in Real estate investment trusts as part of your broader investment strategy:
- Passive Income and Dividends: The primary appeal of REITs is their high dividend yields stemming from steady rental income. REITs are required to pay out at least 90% of taxable earnings to shareholders as dividends annually. This results in dividend yields averaging between 3-10%, which significantly exceeds the ~1.5% yield of the S&P 500 index. REIT dividends can provide stable passive income.
- Diversification: REITs offer portfolio diversification since they invest in real estate instead of stocks and bonds. Real estate performance tends to act independently from stocks and bonds. This offers diversification and risk management benefits. REITs have a low correlation with stocks
- Long-Term Growth: REIT share prices and dividends tend to grow over time as rental income increases. REITs benefit from rising property values and inflation. The FTSE NAREIT All REITs Index has delivered average annual returns of nearly 12% over the past 20 years.
- Accessibility: REITs allow anyone to invest in large-scale commercial real estate projects by purchasing shares. This opens up real estate investing to more investors. Otherwise, individual investors would require huge capital to buy commercial properties outright.
- Liquidity: REIT shares trade on major stock exchanges and can be bought and sold readily, unlike physical real estate assets. This makes REITs more liquid than rental properties.
- Professional Management: REITs are actively managed by real estate professionals. Investors benefit from their real estate expertise like property selection, acquisition, financing, operations, tenant management, and capital management.

Risks and Considerations
While Real estate investment trusts have many advantages, there are also some risks to consider:
- Interest rate risk – REIT’s can be sensitive to interest rate changes which impact financing costs. Rising rates may negatively impact REIT prices.
- Economic risk – An economic downturn could reduce demand for rental space, lower occupancy rates, and hurt REIT dividends.
- Management risk – Poor management can adversely impact the performance of a REIT’s real estate assets.
- Liquidity risk – REIT shares are liquid but less so compared to stocks. Certain REITs have lower trading volumes.
- Tax implications – Some REIT dividends may be considered capital gains taxed at a higher rate than ordinary dividends.
- High yields signify greater risk – Extremely high-yielding REITs carry more risk.
To mitigate risks, invest in diverse REITs across different property sectors and geographic locations. Also assess the REIT’s management experience, portfolio, and financial health.
How to Invest in REITs
If you’re ready to add Real estate investment trusts to your portfolio, here is a step-by-step guide to investing in Real estate investment trusts:
Step 1 – Choose investment account type
REITs can be purchased through taxable brokerage accounts, IRAs, or other retirement accounts like 401(k)s. Consider your goals, taxes, and timeline when choosing an account. Tax-advantaged accounts defer or exempt dividend taxation.
Step 2 – Identify REITs to invest in
Use REIT screeners to filter by criteria like market cap, dividend yield, property type, valuation, debt levels, occupancy rate and narrow down quality REITs to invest in across multiple sectors.
Assess management experience, portfolio holdings growth, dividend history, and risk factors through reviewing financial reports.
Step 3 – Determine investable capital
Consider the size of your overall portfolio and risk tolerance when deciding how much to allocate to REIT investing. Many experts suggest limiting REIT exposure to 10-20% of your total portfolio.
Step 4 – Buy REIT shares
Purchase shares of your selected REITs through a brokerage account. Some brokers like Vanguard and Fidelity allow you to buy and sell REITs commission-free. REIT ETFs like VNQ and SCHH offer instant diversified exposure.
Step 5 – Hold and re-invest
Retain REIT shares long-term to accumulate dividends. Reinvest your dividends using a DRIP to benefit from compound growth over decades. Periodically rebalance holdings back to target allocations.
Key Takeaways on Real Estate Investment Trusts
- REITs provide a simple way to earn passive income and diversify into real estate without buying properties.
- They invest in income-producing properties and are required to pay 90% of earnings as dividends.
- REITs offer average dividend yields of 3-10% that grow over time.
- Invest in multiple REITs across equity and mortgage REITs, property sectors, and regions.
- Limit exposure to 10-20% of your overall portfolio based on risk tolerance.
- Consider REITs for passive income, long-term growth, and portfolio diversification.
REITs can play an important role in income and diversification in an investment portfolio. Do thorough research, understand the risks, and start small. Over time, reinvested REIT dividends can become a significant contributor to investment returns.
